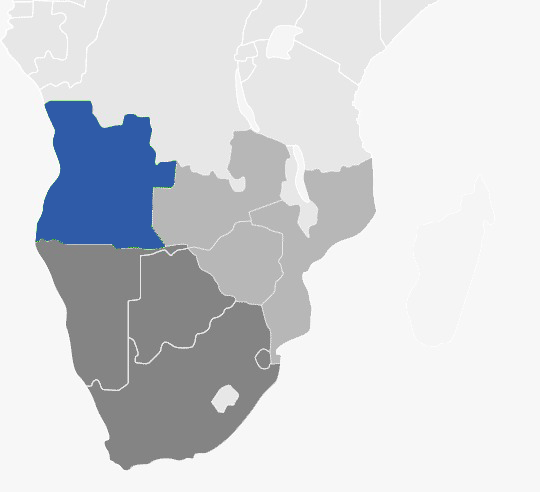
The Republic of Angola is located in Southern Africa surrounded by Namibia to the South, Zambia to the East, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the North. On the western side, the Atlantic Ocean is found. Angola is the second-largest oil producer after Nigeria south of the sahara. Angola has a population of more than 30 million people as of 2018. Luanda is the capital city and the official language is Portuguese. Angola’s economy and GDP is mainly driven by oil.
Angola is reported to have made substantial economic and political progress since the end of the war in 2002. The main developmental challenges are as a result of low oil prices. Angola has steadily developed in the Marine and Coastal Environment, Fisheries and the Petroleum Industry. Angola has been playing a critical role and contributing to the BCC programmes and activities.